If you are a business owner running an online business, you should always be ready to face technical hiccups. Take the example of “Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed”.
We’ve all been there, right? You’re trying to access a website, and BAM! This cryptic message pops up, leaving you wondering what went wrong. It’s like knocking on a door, and instead of someone answering, the whole house just groans.
This error happens when the requested webpage cannot be loaded because the varnish server is unable to retrieve data from the backend server within a specific timeframe. Whether you’re running a WordPress site or any other web platform, this issue can disrupt your online presence.
Don’t you worry! Though this may sound too technical, we will break it down for you in plain English. Through this blog, we will help you understand in detail what this error means, what causes this error, help you in troubleshooting it and steps to avoid this error in future.
What is Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed?
Error 503 – This is an HTTP status code. The “5xx” group of codes means something has gone wrong on the server’s end.
Backend Fetch Failed – This part tells us why the server is grumpy. The “backend” refers to all behind-the-scenes stuff that makes your website work – databases, application logic, and other servers it needs to talk to. “Fetch failed” means the server responsible for getting the information you requested couldn’t do its job.
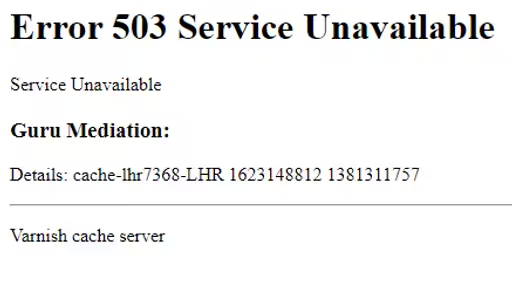
The “Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed” is a specific variant of the HTTP 503 Service Unavailable error generated when the server in the middle (Varnish) failed to retrieve the data from the backend server.
WordPress sites are particularly susceptible to this error when using caching solutions like Varnish, especially during high traffic periowds or when WordPress plugins cause backend delays.
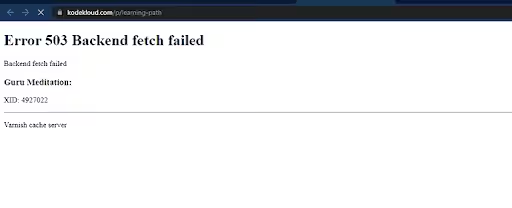
This error is often accompanied by a message like “Guru Meditation – XID -xxxxxx”. The error looks something like this
“Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed
Guru Meditation: XID: xxxxxx”
What are the reasons for this error?
The “Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed” can be triggered due to a variety of reasons. Some of the common issues are listed below –
- Backend Server Unavailability (Too many visitors) – When too many users try to access the website at the same time, it puts load on the web server, ultimately causing the 503-server error.
This may be due to may data requests at the same time or even suspicious spam user attacks on your web application.

Check your Varnish logs to assess the health of the backend server using the command sudo varnishlog -g raw -i backend_health.
If you are still not able to determine the reason for the error, use the command sudo varnishlog -g request -q “RespStatus == 503”. This command will help you identify the specific reason for the 503 Backend Fetch Failed Error.
Related Blog: How to Fix Error 503 in WooCommerce
- Server Connection Timeout – Sometimes the server takes too long to respond to the user request, leading to user’s inability to view the data. For example, the main web server might not be able to communicate effectively with a database server resulting in this error.
- Network Problems – While the 503 error usually points to the server, sometimes the issue can be with the network connectivity between different parts of the backend infrastructure. Network-related issues such as DNS failures or firewall restrictions can break the communication between web servers, leading to server inaccessibility.
- Third Party Service Issues – Modern websites often rely on many external services such as payment gateways, content delivery networks (CDNs), social media integrations, APIs from other companies, etc. If any one of these crucial third-party services goes down or experiences issues, it can prevent the website’s backend from fetching the necessary information, resulting in a 503 error.
- Security Tool Overload- Ad-blockers or security software used on your WooCommerce website might block access to certain content, causing requests to pile up on the server and leading to the error.

- Application Glitches – Websites run on complex code. If there’s a bug in the website’s application code, a problem with a plugin, or an issue with how the application interacts with its database, it can cause the backend processes to fail.

- Configuration Issues – If there are errors in the Varnish configuration file (e.g., default.vcl), it may cause data routing failures.
Troubleshooting Steps to Solve Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed
- Check Backend Server Availability
Check and ensure that the backend server is online and operational –
- Ping Test – Make use of ping command to check if there is server availability issue from the web server provider’s end.
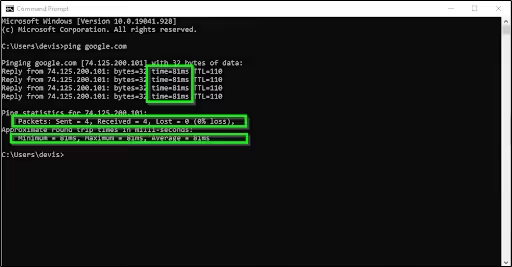
- Direct Access – Try to access the backend server directly through its IP or URL to check for the server’s responsiveness and whether the website data is available upon user request.
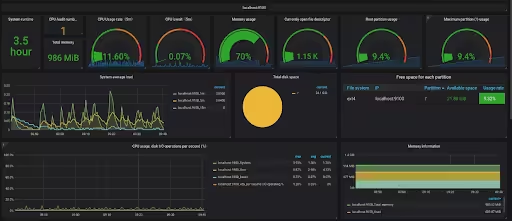
- Monitor Server Load
High traffic can overload servers, causing slow responses or website crashes. To avoid such issues, start monitoring the load on your web server. This will help in pre-empting server issues.
- Scaling Infrastructure – Use load balancers or additional backend servers.
- Caching Mechanisms – Implement caching to reduce backend dependency.
- Monitoring Tools – Use tools like New Relic or Datadog to identify and mitigate website performance bottlenecks.
Master Tip – Try to simulate the high traffic loads through technologies like Locust or Apache JMeter to find server bottlenecks and improve performance.
- Increase Backend Timeout Limits
If the backend is taking too long to respond, increase the timeout limit in your Varnish configuration file (default.vcl).
- Review Varnish Configuration
Ensure that the Varnish configuration file is correctly set up –
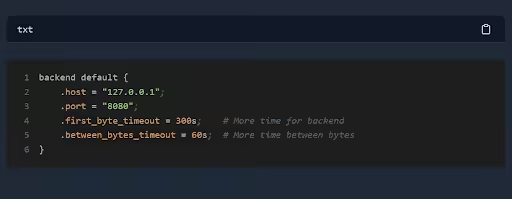
- IP Address, Hostname, and Port – Verify these details in the Varnish configuration file.
- Backend Server Definition – Ensure the backend server is properly defined in the relevant VCL file.
- Check Network Connectivity
Network issues can disrupt communication between servers –
- Packet Loss – Check for packet loss and resolve any network issues.
- DNS Failures – Ensure DNS settings are correct.
- Firewall Restrictions – Verify that firewalls are not blocking necessary traffic.
- Remove Backend Bugs
You can make use of tools like Loggly to study the logs and identify issues causing the error. Once the issue is identified, update the relevant application code to resolve the issue.
Master Tip – Sometimes the issue is temporary in nature and mere rebooting the server or refreshing the page might solve the problem.
- Manage Third-Party Services
Be aware of the reliability of any third-party services that you integrate with your WordPress website. Always have fallbacks available, if possible.
Still struggling with Error 503 despite following these steps? Our WordPress developers can help you diagnose and fix backend issues to keep your site running smoothly.
Also Read: Comprehensive Guide to Resolve WordPress Fatal Errors
Best Practices to Avoid Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed in the Future
To minimize the re-occurrence of Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed, below are some of the best practices that we recommend for your WooCommerce WordPress website–
- Monitor Server Resources –
Regularly check server load and resource utilization to ensure they are adequate for peak traffic. You can make use of tools like NGINX and HAProxy to distribute the server load across different backend servers.
Further, you should regularly check the different server metrics by using tools like Grafana and Prometheus to ensure that the server is functioning optimally.
- Optimize Server Configuration – Ensure that server configurations, including caching and firewall settings are optimized for website performance.
Save static versions of your pages so that people may access them quickly and you don’t have to create them every time they want something. WordPress plugins like WP Super Cache are quite helpful for this.
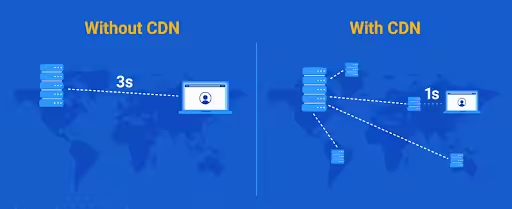
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) – Make use of CDNs to help with distribution of traffic to local servers globally and reduce server load on primary server by serving static content to the users.
- Regular Maintenance – Schedule regular maintenance of web server during off-peak hours to minimize downtime and check for possible errors. It’s much better to have a planned, brief outage than to have random, unpredictable errors throughout the day.
- Content optimization – Try avoiding the use of data-heavy images and content on your website. Make use of the following features for content optimization:
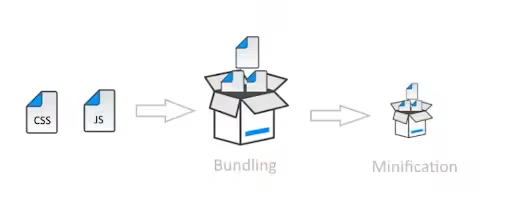
- Minification – Whitespace, comments, and other superfluous components should be eliminated from CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files by minification. You can make use of tools like CSSNano for CSS and UglifyJS for JavaScript.
- File compression – Try to reduce the size of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files. This will speed up the loading of your website by lowering the size of files being sent between the server and users’ browsers.
- Implement Scalability Measures – Having multiple backend servers, multiple caching layers, and even multiple data centers can help ensure that if one component fails, others can pick up the slack to handle an increase in user traffic.
- Performance Testing – Regularly test your website under load to understand its breaking points. Tools like Apache JMeter or similar can help you simulate high traffic and identify potential failure points before they affect real users.
Master Tip – Make use of tools like Pingdom and Uptime Robot to keep an eye on your website around the clock and get notified right away if there are any performance problems or if your site is offline.
Related Blog: How to Perform WordPress Web Maintenance Beyond Updates
Conclusion
The internet is a complex beast, and sometimes things just break. The good news is that 503 errors are almost always temporary. So, take a deep breath, maybe grab a cup of coffee, and try again a little later.
Remember! The Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed is primarily a server-side issue involving the communication between your caching layer and backend servers and may be caused by a single or a combination of issues.
The key is to ensure backend server availability, monitor server load, increase timeout limits, review Varnish configuration, and check network connectivity. This will allow you to mitigate this error and improve your website’s reliability and accessibility to users.
And last and most importantly, regular monitoring of your WordPress website can be the best defense against such server errors.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed a client-side or server-side issue?
Error 503 is a server-side issue, indicating a problem with the server or its configuration.
- Is the “Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed” the same as a regular 503 error?
Not exactly. While both are HTTP 503 status codes, the “Backend Fetch Failed” variant specifically indicates a problem with communication between a caching server (like Varnish) and the backend server. A regular 503 error can have many different causes and doesn’t necessarily involve a caching layer.
- How long does Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed usually last?
The timing varies greatly. The error could only be for a few seconds if the server was just momentarily overloaded or restarting. It could even be for minutes or even hours if it’s due to more significant maintenance, a serious application bug, or a major outage.
- Can the SEO of my website be impacted by Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed?
The Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed typically has little effect on SEO if it occurs occasionally and is promptly fixed. The user experience and search engine indexing of your WooCommerce website may suffer if the issue continues for an extended length of time, which may ultimately lower your site’s ranking in search results.
- Can Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed be caused by a DDoS attack?
Yes, Error 503 Backend Fetch Failed can be caused by a DDoS attack. In a DDoS attack, your website server will receive a large number of requests at once, overwhelming its capacity to manage the genuine user traffic.
- As a website owner, how can I be notified quickly if my site is showing a 503 error?
You can make use of uptime monitoring services with many free and paid options available online. These services regularly ping your website from different locations and can alert you via email, SMS, or other channels if it becomes unavailable or returns an error like 503.
- If I see a 503 error, does it mean the website is gone forever?
Not at all! It simply means the server is temporarily unable to handle the request.

