Hello there, fellow coder! 👋 Have you been in the website building zone only to be rudely kicked out by a “JavaScript heap out of memory” error? Now, that’s something that can put a serious stop to your website development process. No need to stress out! Don’t worry. You are not the only one dealing with this problem. We’ve all been there.
Whether you’re building custom WordPress themes, developing complex WooCommerce plugins, or creating dynamic e-commerce solutions, JavaScript heap memory errors can strike at the most inconvenient times.
Our blog will try its best to help you understand and resolve that pesky heap memory error. We will explain to you the JavaScript heap memory errors, their primary causes, and how they can be solved using practical, applicable problem-solving methods.
What is JavaScript Heap, and JavaScript Heap Memory Error?
Think of the JavaScript heap as a big, unstructured memory playground. When you create objects, arrays, or functions in your code, they get stored in this space. Unlike the stack, which is for static data like numbers and strings, the heap is for dynamic data that can grow and shrink as your application runs.
The dreaded “Fatal Error: Reached Heap Limit Allocation Failed – JavaScript Heap Out of Memory” message appears when your application tries to use more memory than what’s available in the heap. It is basically JavaScript’s way of saying, “I’ve run out of space in my playground!”.
By default, Node.js sets pretty conservative memory limits. On 32-bit systems, you get about 700 MB, while 64-bit platforms allow up to 1400 MB. These limits exist for good reasons, but sometimes your application legitimately needs more space to operate.
Related Blog: Fix JavaScript Fatal Errors: Your Go-To Guide
Common Causes of JavaScript Heap Memory Errors
Understanding the root causes helps you prevent these errors from happening in the first place. Let’s take a look at the main factors causing the Heap Memory Errors in JavaScript:
- Handling Massive Amounts of Data: Trying to load and process a huge file or a massive dataset all at once is a classic recipe for disaster. We’re talking about huge arrays with thousands of elements, complex objects with countless properties, or large files like images, videos, and extensive JSON or CSV datasets. The heap can quickly get burdened due to such a large data size.
- Memory Leaks: These are the silent assassins of your application’s memory. A memory leak happens when memory is allocated but never released, even though it’s no longer needed. Common causes of memory leaks in JavaScript Heap Memory include:
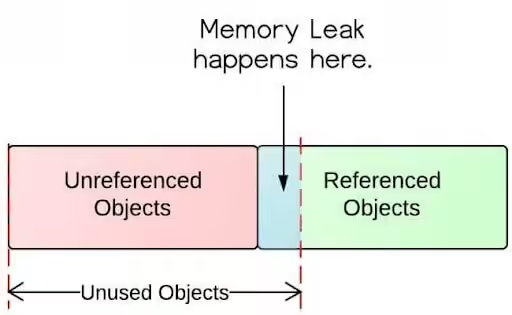
- Lingering Global Variables: Declaring variables in the global scope can prevent them from being garbage collected, even after they’re no longer in use.
- Event Listeners Gone Rogue: If you add an event listener to an element but forget to remove it when the element is no longer needed, it can keep that element and its associated memory from being released.
- Clumsy Closures: Closures are a powerful feature, but they can sometimes accidentally hold on to variables from their parent scopes, preventing them from being garbage collected.
- Forgotten Timers: setInterval and setTimeout functions that are never cleared can also lead to memory leaks in JavaScript Heap Memory.
- Inefficient Code and Sneaky Loops: An infinite loop or a poorly written recursive function without a proper exit condition can consume memory at an alarming rate.
- Node.js Version: Something that WP developers often tend to overlook is installing a 32-bit version of Node.js on a 64-bit machine. This can artificially limit your available memory. Always check that your Node.js version matches your system architecture. For complex enterprise applications experiencing persistent memory issues, consulting with a Node js development company can provide specialized expertise in architectural optimization and memory profiling.
People Also Read: How to Increase WordPress Memory Limit
Your Toolkit for Fixing Heap Memory Errors in JavaScript
This is where the fun part begins. Once you have identified the problem, it’s time to fix it! Here are some practical solutions to get your application running smoothly again.
- The Quick Fix: Increase the Limit in JavaScript Heap Memory
One of the quickest and easiest ways to solve the JavaScript heap memory error problem. You can increase the default heap memory size for your Node.js v8 and above application by using th— -max-old-space-size flag when you run your script:
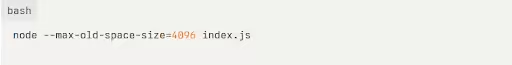
This command will set the heap size to 4GB. You can adjust the number based on your application’s needs and your system’s available RAM size.
You can also set this memory limit globally for all Node.js applications using environment variables as detailed below. This will help you to bypass the default ~1.5GB limit during memory-intensive tasks like ng build.

Pro tip: The thumb rule to set your memory limit is to use 75% of your available RAM. For instance, if your RAM size is 4 GB, you can set this limit to 3072, i.e., 4 GB. This will leave sufficient space for the operating system and other processes to function correctly.
- The Smarter Fix: Optimize Your Code
The best long-term solution is to write more memory-efficient code. Here’s how:
- Stream Large Datasets: Instead of loading a huge file into memory all at once, use streams to process it in smaller, more manageable chunks.

- Avoid Global Variables When Possible: Keep your variables scoped to the functions where they are needed. This helps the garbage collector do its job effectively.
- Clean Up Your Event Listeners: Always remember to remove event listeners when the element they’re attached to is no longer needed.

- Be Mindful of Closures: Understand what variables your closures are holding on to and make sure they aren’t unintentionally keeping large objects in memory.
- Clear Your Timers: If you use setInterval, make sure you have a corresponding clearInterval when you’re done. The same goes for setTimeout and clearTimeout.
- Make use of Process Managers:
Tools like PM2 can automatically restart your application in case it runs out of memory. While this doesn’t solve the underlying problem, it prevents extended downtime.

- The Detective Work: Use Browser DevTools
Your browser’s developer tools are your best friend when it comes to hunting down memory leaks in JavaScript heap Memory. Here’s a quick guide to using the Chrome DevTools:
- Open the Performance Tab: Record a performance profile while you interact with your application. Look for a “sawtooth” pattern in the memory graph, which indicates normal memory allocation and garbage collection. If you see a steady increase in memory usage that never drops, you might have a leak.
- Take Heap Snapshots: Go to the Memory tab and take a heap snapshot. Then, perform some actions in your application and take another snapshot. You can then compare the two snapshots to see which objects are being created and not being garbage collected.
- Look for Detached DOM Trees: In the heap snapshot, filter for “Detached”. This will show you DOM elements that have been removed from the page but are still being held in memory by a JavaScript reference.
- Garbage Collection Tuning:
Node.js uses V8’s garbage collector by default. However, you can optimize its behavior. The max_semi_space_size flag controls the size of the young generation heap. When you increase this value, it can help improve performance for applications that create many short-lived objects.
- Use an Efficient Algorithm and Data Structures:
- Reuse the objects: Try to minimize the new objection creation in loops. Use the following to do so.

- Prefer arrays / typed arrays: Arrays or typed arrays are more memory-efficient than complex objects. Try to use them to the extent possible.
- Limit recursion depth: Implement exit conditions in recursive functions to avoid creating of loop.
- Object Pooling:
You should recycle the frequently created or destroyed objects to avoid allocation overhead.

People Also Read: Comprehensive Guide To WordPress Memory Management
Best Practices to Avoid Recurrence of JavaScript Heap Memory Errors
- Limit the Global Variables:
- Avoid storing large data in the global scope. You can make use of local variables or modules to contain references.
- Replace var with let / const for block-scoping to enable automatic garbage collection.
- Optimize Closures and References:
- Avoid closures that trap large objects and nullify external references when unused.
- Use WeakMap / WeakSet for caches to allow garbage collection of keys as provided below:

- Memory-Efficient Data Structures:
- Prefer typed arrays (Float64Array) over generic objects for numerical data. This will save a lot of space for you to perform other functions.
- Try to reuse objects in loops instead of recreating them.
- Lazy Loading and Code Splitting:
- Dynamically load modules with import() to reduce the initial memory footprint.
- Split bundles via Webpack / Rollup for on-demand resource loading.
Conclusion
JavaScript heap memory errors can be a real headache, but these errors can be resolved. By understanding what causes them and how to debug them, you can keep your applications running efficiently.
For businesses investing in WooCommerce development services addressing these memory issues is crucial for maintaining optimal site performance, especially when dealing with large product catalogs, complex checkout processes, or high-traffic e-commerce platforms.
Remember to be proactive about memory management in your code, and don’t be afraid to dive into your browser’s developer tools to investigate and resolve issues in JavaScript heap Memory.
Most importantly, remember that encountering these errors doesn’t mean you’re a bad developer – it simply means you’re working on applications complex enough to push system boundaries. That’s actually pretty exciting! Happy coding! 🚀🚀🚀
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A. What is the difference between the stack and the heap in JavaScript?
The stack is used for static memory allocation and stores primitive types (like numbers and strings) and references. It’s fast and has a fixed size.
The heap is used for dynamic memory allocation and stores objects and functions. It’s larger and more flexible than the stack.
B. Is increasing the memory limit always a good solution?
Increasing the memory limit can be a temporary fix, but it’s often a sign of an underlying issue like a memory leak or inefficient code. It’s always better to investigate and fix the root cause.
C. How does garbage collection work in JavaScript?
JavaScript has an automatic garbage collector that periodically looks for memory that is no longer reachable from the root of the application. When it finds unreachable objects, it frees up that memory.
D. Is it safe to set max-old-space-size higher than my available RAM?
No, if you do so, it may cause system instability. Setting the limit higher than available RAM may cause your system to swap memory to disk or kill processes. As a rule of thumb, you can use about 75% of your available RAM size.
E. Can I completely prevent memory leaks?
While you can’t eliminate memory leaks in JavaScript Heap Memory completely, adhering to best practices in coding and regularly testing your application’s performance can help reduce their occurrence significantly.



